While workers worry about job security, investors anticipate significant AI-driven changes to labor market in 2026, with venture capitalists predicting shifts from human hiring to AI investments as TechCrunch survey highlights enterprise VCs expecting automation of repetitive and logical roles potentially leading to layoffs or higher productivity through systematic AI labor market transformation. This isn’t just technology trend, it’s fundamental restructuring of employment economics through comprehensive AI labor market transformation.
Here’s what separates AI realists from AI optimists: while your employees hope for augmentation, VCs like Eric Bahn from Hustle Fund foresee unclear but major labor impacts while Marell Evans of Exceptional Capital predicts companies reallocating budgets from labor to AI, accelerating U.S. layoffs through anticipated AI labor market transformation.
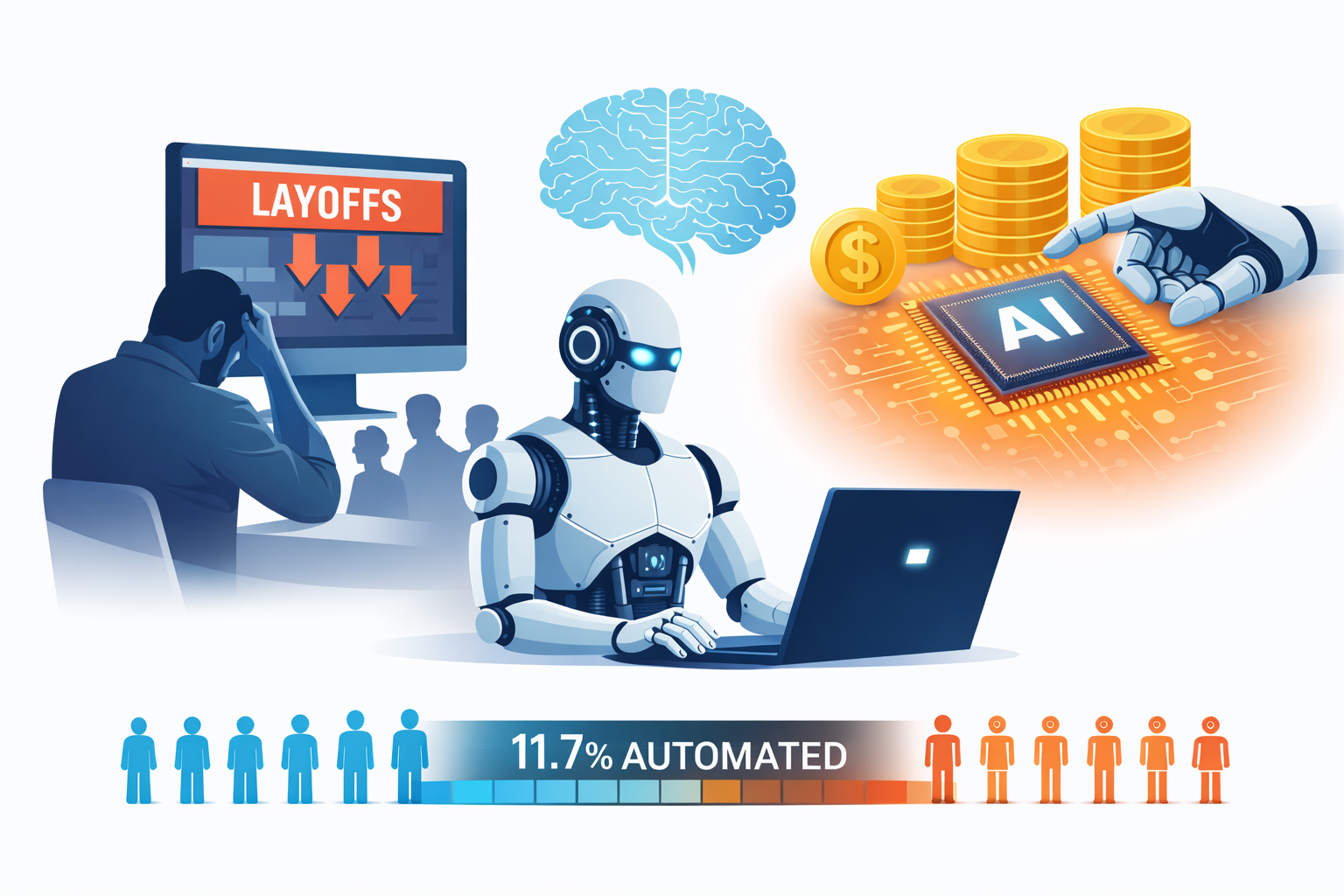
The result? Jason Mendel at Battery Ventures calls 2026 the “year of agents” where AI automates entire tasks rather than just aiding humans, while November MIT study estimates 11.7% of jobs could already be automated by current AI, proving that AI labor market transformation doesn’t represent distant future, it’s imminent reality through immediate AI labor market transformation.
The AI Labor Market Transformation Crisis That’s Redefining Employment Economics
When venture capital investors predict significant AI-driven changes to labor market in 2026, they’re not just forecasting technology adoption, they’re fundamentally anticipating how employment economics shift from human hiring to AI investment through strategic AI labor market transformation.
The scope of AI labor market transformation becomes evident through TechCrunch survey where enterprise VCs expect automation of repetitive and logical roles that comprise substantial portion of current employment through widespread AI labor market transformation.
Investor predictions about AI labor market transformation carry weight because VCs fund companies implementing automation while observing hiring patterns across portfolio companies through informed AI labor market transformation.
The transformation proves that AI labor market impact isn’t theoretical concern debated by academics, it’s business reality shaping capital allocation decisions through practical AI labor market transformation.
How Capital Allocation Shifts Drive AI Labor Market Transformation
Most companies historically allocated budgets primarily to labor costs, while investors predict fundamental shift where companies reallocate budgets from labor to AI investment through capital-driven AI labor market transformation.
The power of this capital reallocation in AI labor market transformation becomes evident through Marell Evans’ prediction that budget shifts will accelerate U.S. layoffs as companies choose AI over human hiring through financial AI labor market transformation.
Their approach to AI labor market transformation reflects investor observation that AI investment provides better returns than human hiring for repetitive and logical tasks through economically-rational AI labor market transformation.
When companies face choice between hiring humans or investing in AI, economic incentives increasingly favor automation through cost-driven AI labor market transformation.
The Agent Economy That AI Labor Market Transformation Enables
Perhaps the most significant prediction for AI labor market transformation is Jason Mendel’s characterization of 2026 as “year of agents” where AI automates entire tasks rather than just assisting humans through autonomous AI labor market transformation.
This agent evolution in AI labor market transformation represents shift from AI as tool to AI as worker that performs complete functions independently through capable AI labor market transformation.
The agent-driven AI labor market transformation demonstrates how technology progresses from augmentation to replacement when AI can handle entire workflows without human intervention through advanced AI labor market transformation.
The organizations deploying agents for AI labor market transformation will achieve cost structures that human-dependent competitors cannot match through automated AI labor market transformation.
The Automation Potential That AI Labor Market Transformation Reveals
The quantified scale of AI labor market transformation comes from MIT study estimating 11.7% of jobs could already be automated by current AI, representing substantial wages at risk through measurable AI labor market transformation.
This automation potential in AI labor market transformation demonstrates that displacement threat doesn’t require future AI advances, current technology suffices for significant employment impact through present AI labor market transformation.
Supporting evidence for AI labor market transformation includes employers eliminating entry-level positions and citing AI in layoffs at firms like Workday, Amazon, and Microsoft through documented AI labor market transformation.
When 11.7% automation potential exists with current technology, future AI advances could expand displacement considerably through accelerating AI labor market transformation.
The HR Leader Perspective On AI Labor Market Transformation
The management view of AI labor market transformation shows nearly 90% of senior HR leaders expect AI to reshape jobs in 2026, demonstrating that workforce planning professionals anticipate fundamental changes through leadership-recognized AI labor market transformation.
This HR consensus about AI labor market transformation suggests that employment changes represent strategic initiatives rather than accidental consequences of technology adoption through intentional AI labor market transformation.
Senior leaders’ expectations for AI labor market transformation indicate that job reshaping will occur deliberately as companies implement workforce strategies incorporating automation through planned AI labor market transformation.
When HR leadership overwhelmingly expects AI labor market transformation, employees should prepare for substantial changes regardless of company reassurances through realistic AI labor market transformation.
The Productivity Versus Displacement Debate In AI Labor Market Transformation
The controversial aspect of AI labor market transformation involves whether automation causes layoffs, boosts productivity, or augments workers as Eric Bahn questions through uncertain AI labor market transformation.
This ambiguity in AI labor market transformation reflects genuine uncertainty about whether companies will reduce headcount, maintain workforce while improving output, or enable existing workers to handle more through varied AI labor market transformation.
AI proponents claim that AI labor market transformation shifts workers to higher-skilled “deep work” by handling repetitive tasks rather than eliminating roles outright through positive AI labor market transformation.
The actual outcome of AI labor market transformation likely varies by company, industry, and economic conditions rather than following single pattern through diverse AI labor market transformation.
The Counterarguments Against AI Labor Market Transformation
The skeptical perspective on AI labor market transformation argues that fears of mass job losses are overblown with AI reshaping tasks amid broader economic factors like weakening markets through moderated AI labor market transformation.
This counter-narrative to AI labor market transformation suggests that technology gets blamed for employment changes actually caused by economic cycles or business strategy through attributed AI labor market transformation.
Some experts predict that AI labor market transformation creates new opportunities in AI oversight and collaboration, though reskilling remains critical through opportunity-creating AI labor market transformation.
When critics question AI labor market transformation severity, they provide alternative interpretation where technology enables rather than eliminates employment through optimistic AI labor market transformation.
The Reskilling Challenge Within AI Labor Market Transformation
The workforce adaptation dimension of AI labor market transformation requires reskilling programs that enable workers to transition from automated roles to AI-adjacent positions through educational AI labor market transformation.
This reskilling necessity in AI labor market transformation demonstrates that employment protection requires proactive capability development rather than hoping automation won’t affect specific roles through prepared AI labor market transformation.
The challenge of AI labor market transformation includes speed of change potentially exceeding retraining capacity, leaving workers unable to adapt quickly enough through overwhelming AI labor market transformation.
When AI labor market transformation requires widespread reskilling, success depends on whether training programs can prepare workers faster than automation eliminates roles through competitive AI labor market transformation.
The Entry-Level Elimination Within AI Labor Market Transformation
The career development impact of AI labor market transformation includes employers eliminating entry-level positions that traditionally provided career entry points through structural AI labor market transformation.
This entry-level elimination in AI labor market transformation creates particular challenge because it removes stepping stones for workers building careers through career-path-disrupting AI labor market transformation.
The long-term consequences of AI labor market transformation could include reduced career mobility as fewer workers gain foundational experience needed for advancement through mobility-limiting AI labor market transformation.
When entry-level positions disappear through AI labor market transformation, career pathways that depend on foundational roles become blocked through systemic AI labor market transformation.
The Economic Context Amplifying AI Labor Market Transformation
The broader environment for AI labor market transformation includes weakening markets and economic pressures that make automation more attractive than during growth periods through economically-driven AI labor market transformation.
This economic amplification of AI labor market transformation suggests that displacement accelerates during downturns when companies seek cost reduction through opportunistic AI labor market transformation.
The timing of AI labor market transformation during economic uncertainty means that multiple factors combine to pressure employment beyond just technology through compounded AI labor market transformation.
When economic pressures combine with AI capabilities for AI labor market transformation, displaced workers face particular challenges finding alternative employment through difficult AI labor market transformation.
The Investment Strategy Implications Of AI Labor Market Transformation
The capital allocation dimension of AI labor market transformation shows investors directing funds toward automation technologies rather than labor-intensive businesses through investment-driven AI labor market transformation.
This investment pattern in AI labor market transformation creates self-fulfilling prophecy where capital availability accelerates automation adoption through funded AI labor market transformation.
Venture capitalists’ predictions about AI labor market transformation influence startup strategies and corporate priorities because founders and executives seek investor approval through investor-shaped AI labor market transformation.
When investment community expects AI labor market transformation, their capital allocation decisions ensure that prediction materializes through capital-driven AI labor market transformation.
The Strategic Response To AI Labor Market Transformation
The 2026 AI labor market transformation predictions provide crucial insights for workers and policymakers. First, acknowledge that substantial employment displacement appears likely based on investor and HR leader consensus through realistic AI labor market transformation.
Second, recognize that reskilling urgency increases as automation capabilities advance faster than workforce adaptation through accelerating AI labor market transformation.
Third, understand that economic pressures amplify AI labor market transformation as companies choose automation during cost-cutting periods through economically-pressured AI labor market transformation.
Fourth, prepare for “year of agents” where AI automates entire tasks rather than just assisting, requiring workforce responses beyond tool adoption through agent-driven AI labor market transformation.
The Employment Future Amid AI Labor Market Transformation
The labor market evolution through AI labor market transformation represents defining challenge requiring coordinated response from workers, employers, and policymakers. The question isn’t whether AI will transform employment but how quickly and whether society can manage transition through managed AI labor market transformation.
AI labor market transformation isn’t just technological shift, it’s economic and social transformation requiring policy responses including workforce retraining, social safety nets, and potential reforms addressing automation’s distributional effects through comprehensive AI labor market transformation.
The time for honest AI labor market transformation discussion is now. The societies addressing automation’s employment impact proactively will better manage transition than those denying systematic workforce changes through prepared AI labor market transformation.
The investor predictions for 2026 AI labor market transformation, backed by MIT automation estimates and HR leader expectations, suggest imminent substantial employment changes. The only question is whether we’ll manage this transition responsibly through workforce support and policy reform or allow market forces alone to determine outcomes affecting millions of workers, families, and communities through unmanaged AI labor market transformation.